Legg Perthes Disease Treatment
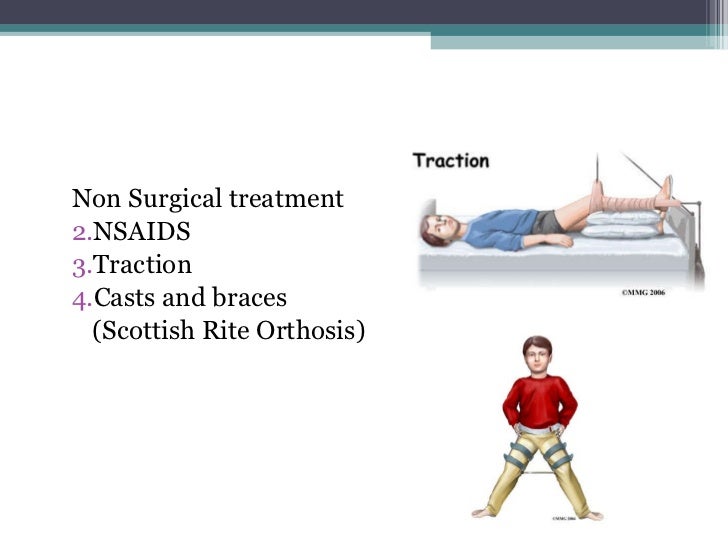
Legg perthes disease treatment. In mild cases of Legg-Calve-Perthes disease vets may treat conservatively with rest and pain medications this may include anti-inflammatory drugs. Goals in the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease LCPD include the following. The natural history or what would happen if nothing is done is generally poor unless the disease is mild.
Salters innominate osteotomy was initially developed for the treatment of congenital hip dislocations 59. The primary goal of treatment for Perthes disease is to help the femoral head recover and grow to a normal shape. Treatment is age-dependent.
Salter applied this treatment to LCPD to surgically contain the femoral head when extrusion was present 60. Children. Bed rest and abduction stretching exercises are recommended.
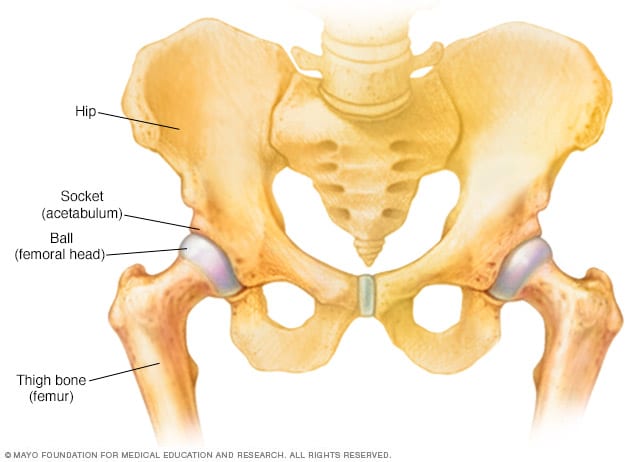
The way that surgeons achieve this goal is using a concept called containment. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease does not require emergent inpatient care. Non Operative Treatment - Discussion - principles of treatment are maintenance of ROM.
O tratamento da moléstia de Legg-Calvé-Perthes visa obter uma cabeça femoral congruente e com a forma mais esférica possível. Containment and surgical treatment supports the concept that containment is a key factor in the treatment of Legg-Perthes disease. A história natural mostrou que a maioria dos casos evolui satisfatoriamente sem tratamento.
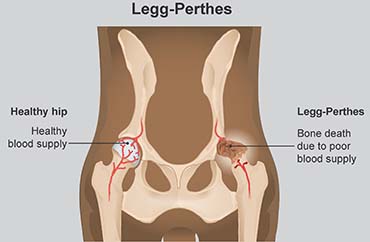
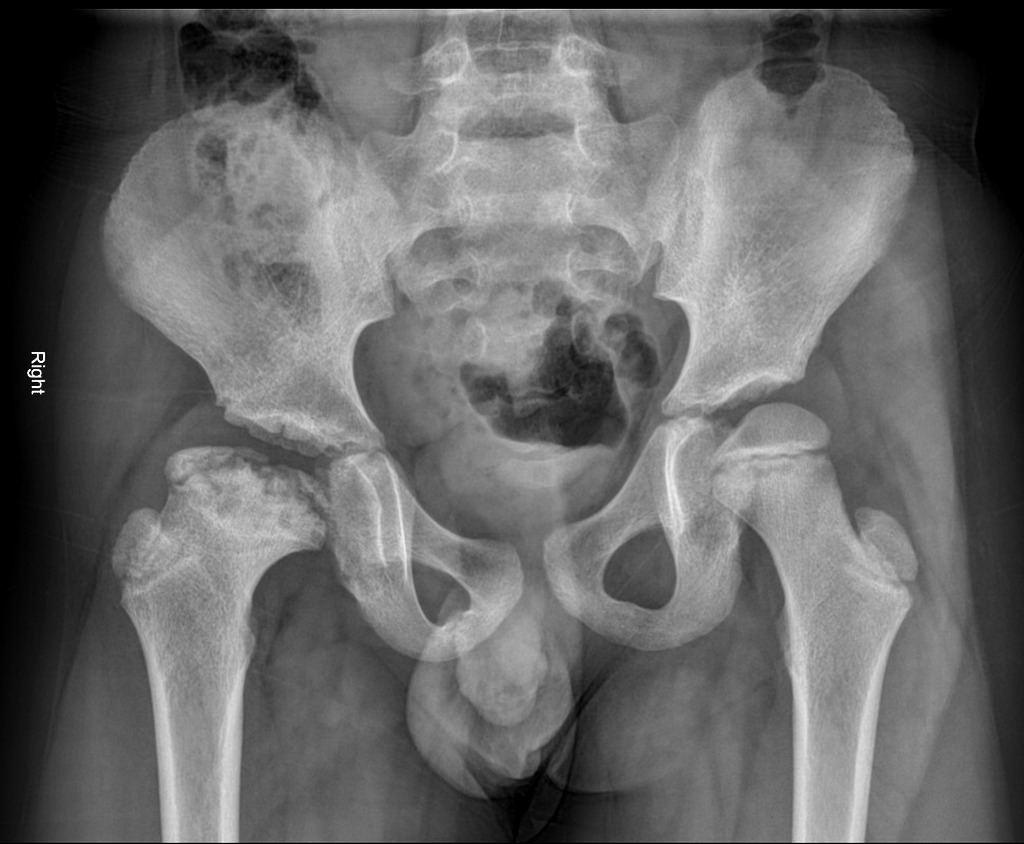
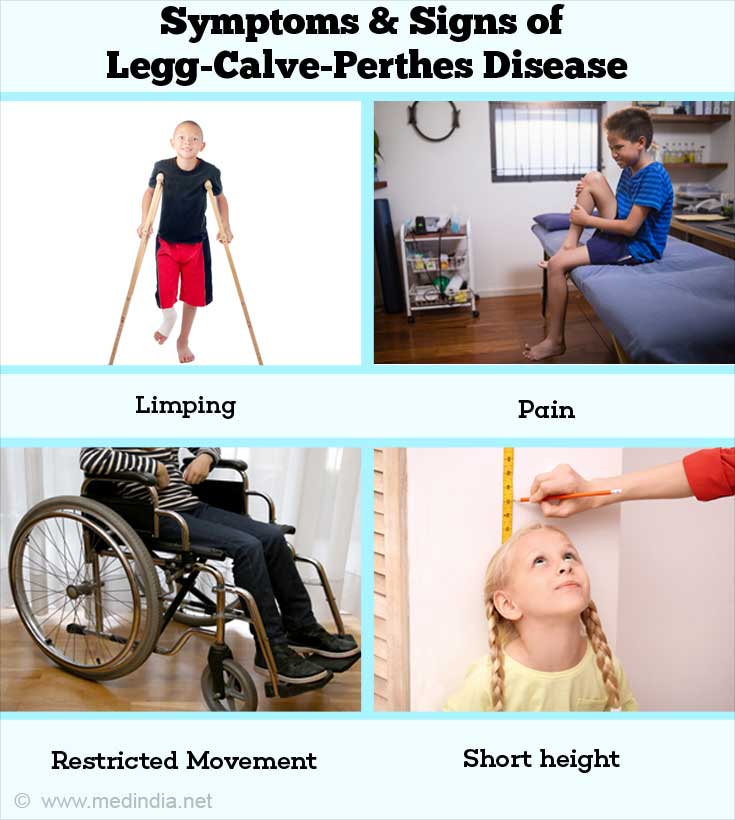
A short period of rest is recommended during acute exacerbations. Initially close follow-up is required to determine the extent of necrosisTreatment may involve observation usually in children younger than 6 years. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease is a juvenile form of idiopathic osteonecrosis of the femoral head that can lead to permanent femoral head deformity and premature osteoarthritis.
Kids diagnosed with Perthes after age 8 have the most guarded long term outlook. The closer to normal the femoral head is when growth stops the better the hip will function in later life.
Eliminating hip irritability Restoring and maintaining good range of motion in the hip.
Treatment is age-dependent. The natural history or what would happen if nothing is done is generally poor unless the disease is mild. Initially close follow-up is required to determine the extent of necrosisTreatment may involve observation usually in children younger than 6 years. Children. Legg Calve Perthes Disease. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease does not require emergent inpatient care. A história natural mostrou que a maioria dos casos evolui satisfatoriamente sem tratamento. Up to now different surgical and nonsurgical treatments including femoral varus osteotomy innominate osteotomy pelvic osteotomies triple osteotomy Chiari osteotomy and shelf acetabuloplasty have been suggested for noncontainable LCPD hips. Goals in the treatment of Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease LCPD include the following.
Any acute pain should be managed with NSAIDs or paracetamol. Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease does not require emergent inpatient care. Salter applied this treatment to LCPD to surgically contain the femoral head when extrusion was present 60. Children. O papel do cirurgião é identificar os casos em torno de 20 que se beneficiarão com o tratamento. Eliminating hip irritability Restoring and maintaining good range of motion in the hip. Up to now different surgical and nonsurgical treatments including femoral varus osteotomy innominate osteotomy pelvic osteotomies triple osteotomy Chiari osteotomy and shelf acetabuloplasty have been suggested for noncontainable LCPD hips.


/perthes-disease-4174322_FINAL-5c05c1c546e0fb0001f4a111.png)














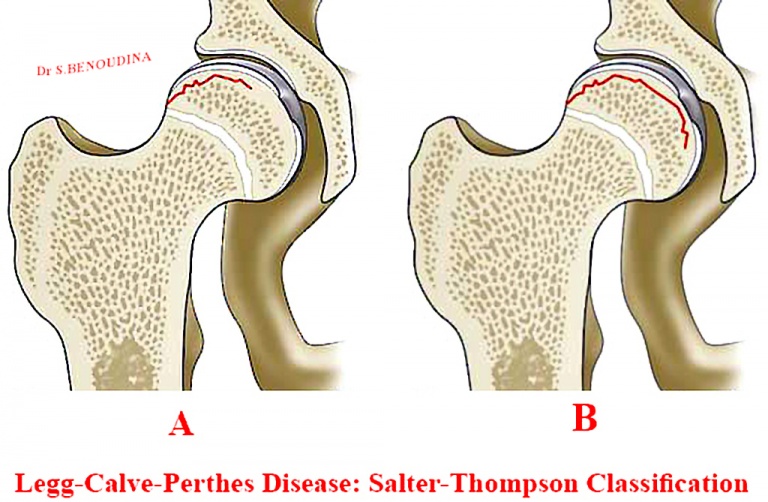

















Post a Comment for "Legg Perthes Disease Treatment"