Renal Artery Stenosis Treatment Guidelines
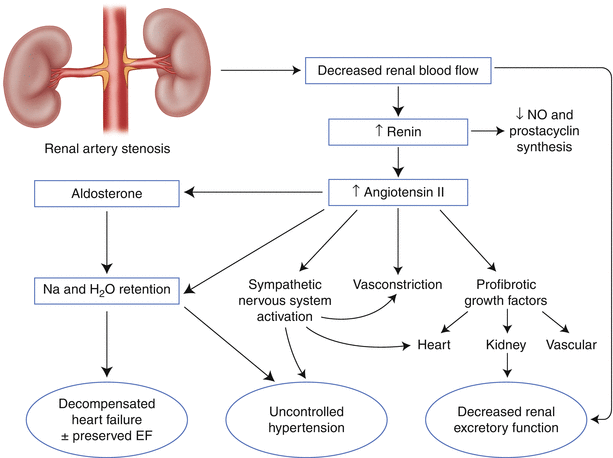
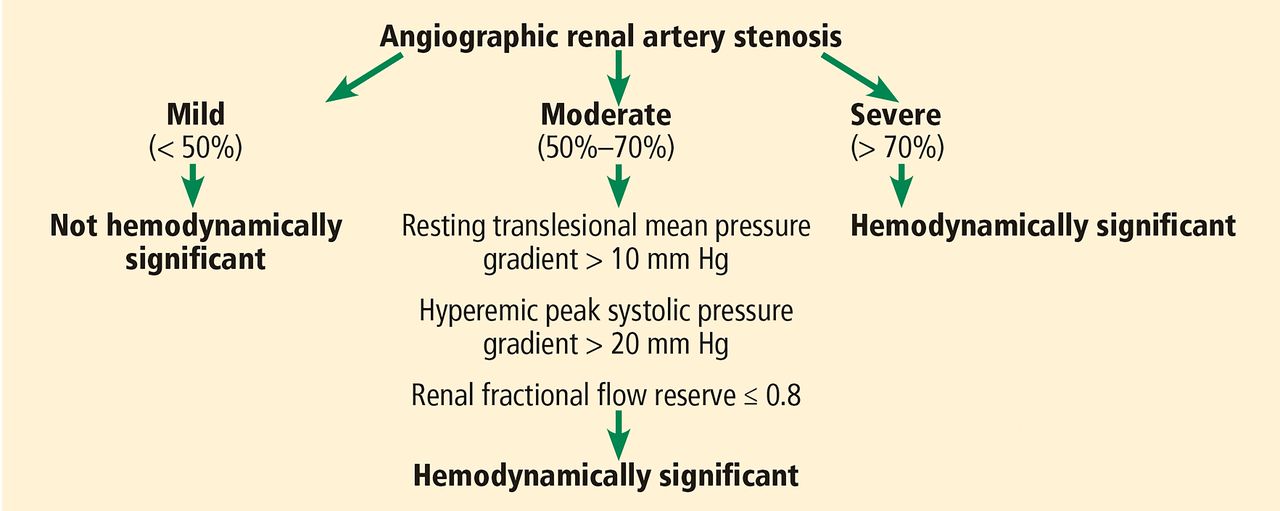
Renal artery stenosis treatment guidelines. The following organizations have released guidelines for the management of renal artery stenosis RAS. It is considered angiographically significant if more than a 50 reduction in vessel diameter is present. RAS is associated with three major clinical syndromes.
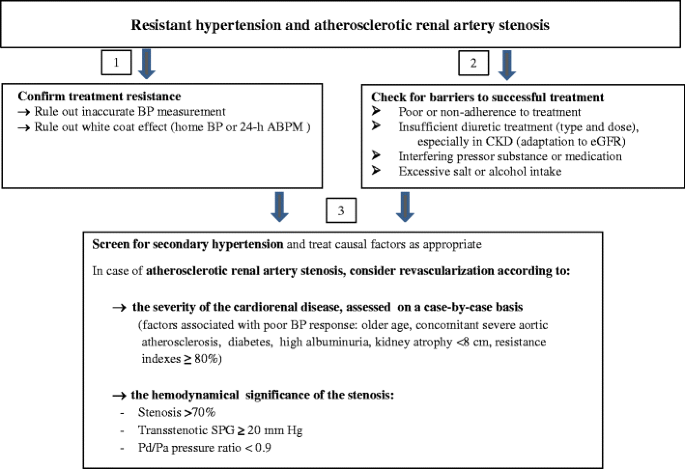
In case of bilateral narrowing or in a stenotic solitary kidney renal insufficiency eg. 12 However much information on the prevalence of renal artery disease has been derived from studies of patients. Severe renal artery stenosis may cause renovascular hypertension.
August 22 2014 Source. One of the first ways to treat this condition is with medications. The European Stroke Organization ESO.
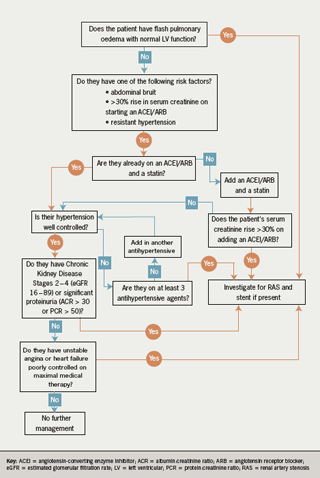
RAS that has not led to RVH or caused a significant blockage of the artery may not need treatment. Practice Parameters and Technical Standards are not inflexible rules or requirements of practice and are. In the Cardiovascular Health Study of an elderly population with mean age 77 years the prevalence of renal artery disease defined as stenosis reducing arterial diameter by 60 or occlusion was 91 in men and 55 in women.
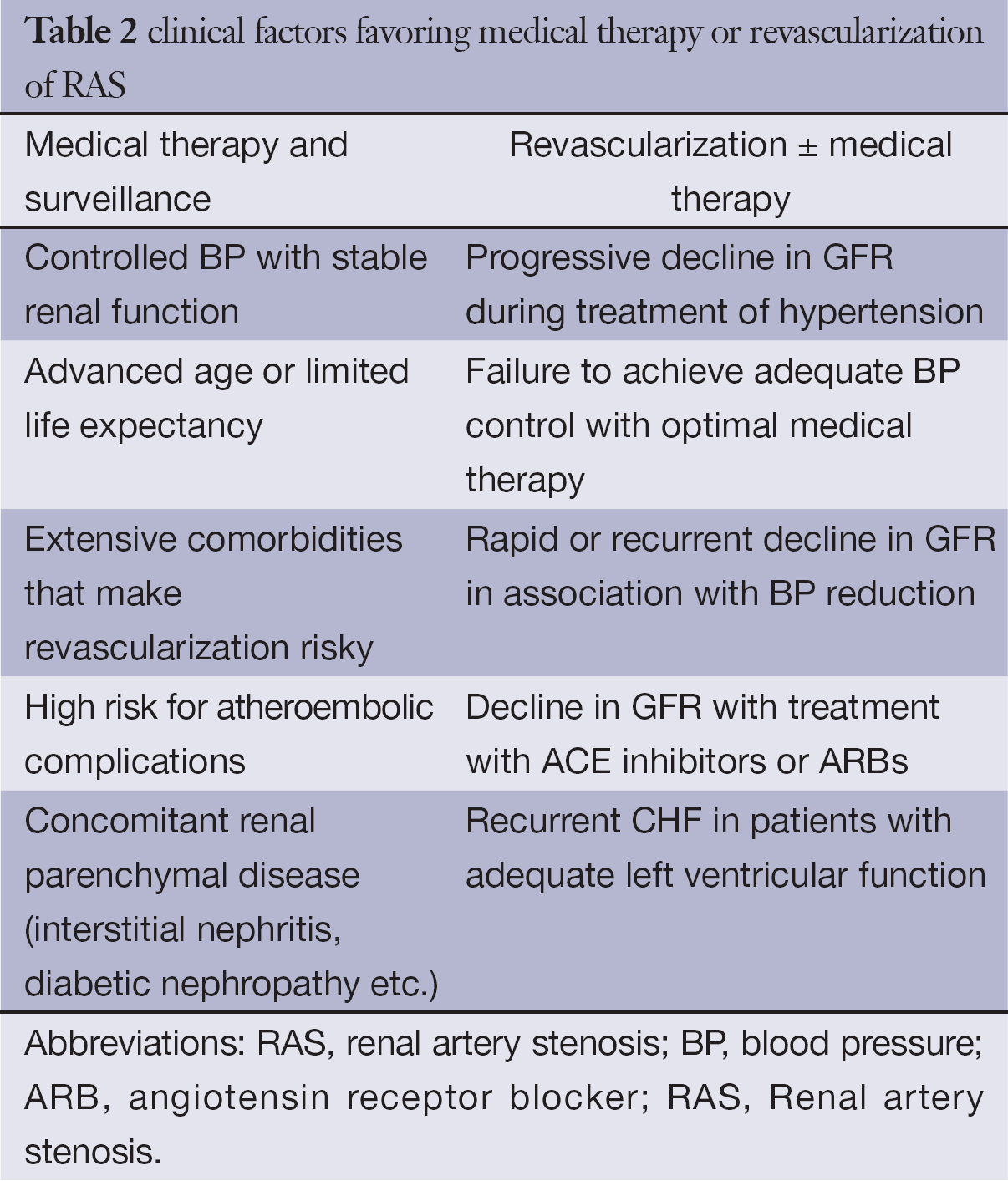
Safian RD Textor SC. Evidence supporting various strategies is then presented followed by a review of formal guidelines. Relieve the blockage of the renal arteries.
Renal artery stenosis can be treated by revasularization using either percutaneou. Document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral mesenteric renal upper and lower extremity arteries Endorsed by. Even if you take medications for RAS and other underlying conditions certain lifestyle changes can.
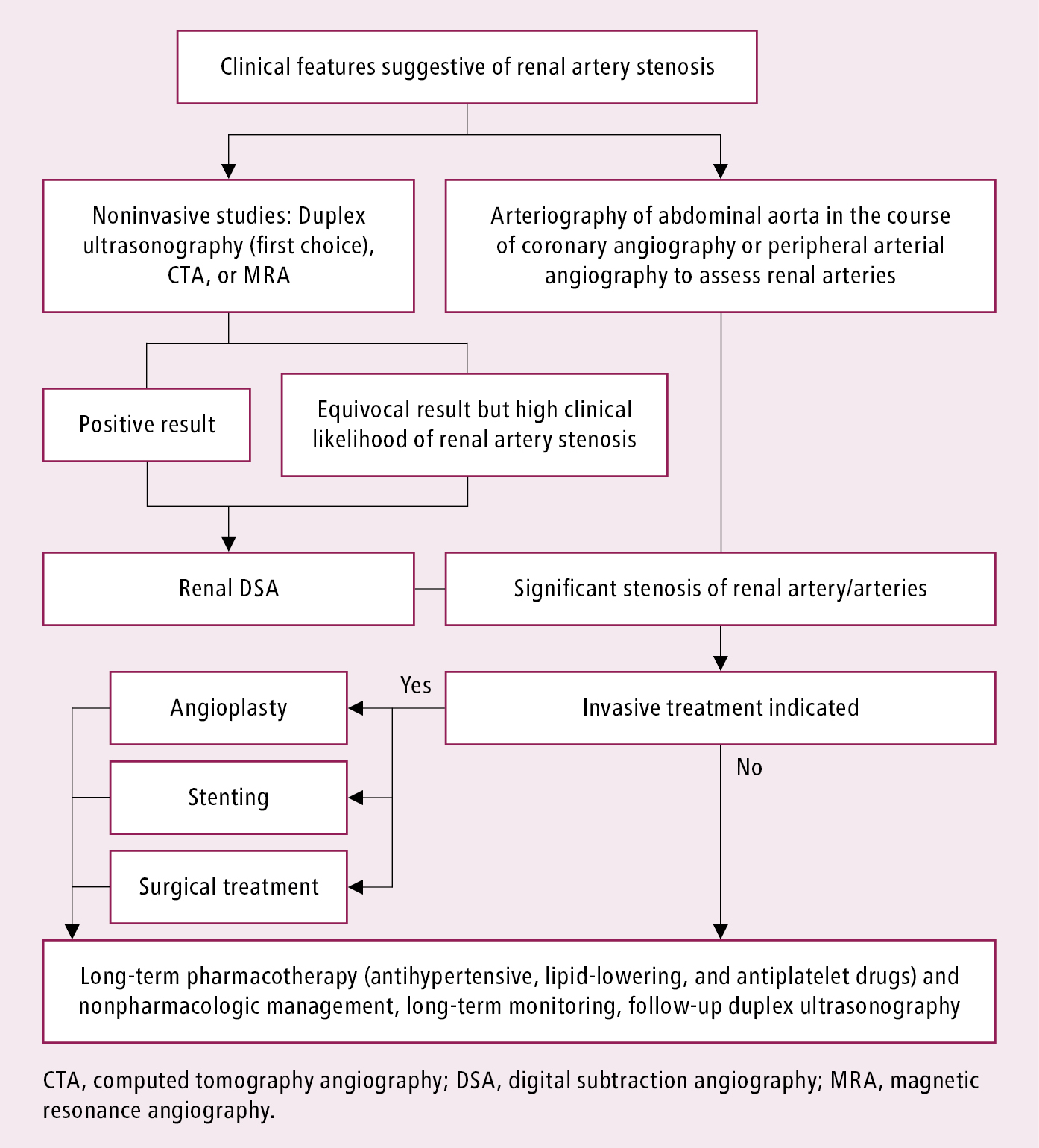
How is renal artery stenosis treated. Surgical revascularization should be considered in case of complex lesions less amendable to angioplasty stenosis associated with complex aneurysm and restenosis despite 2 unsuccessful attempts of.
In case of bilateral narrowing or in a stenotic solitary kidney renal insufficiency eg.
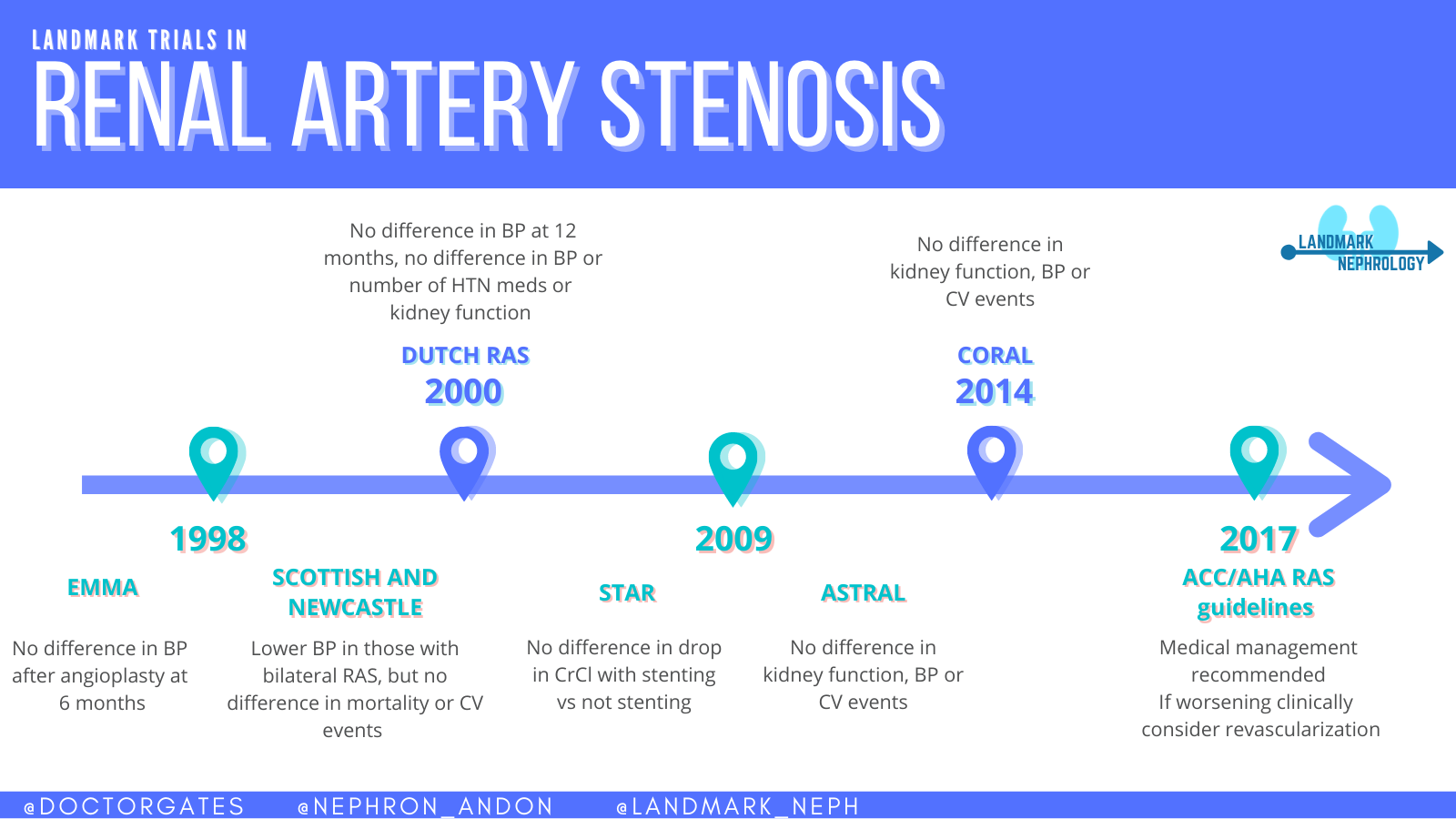
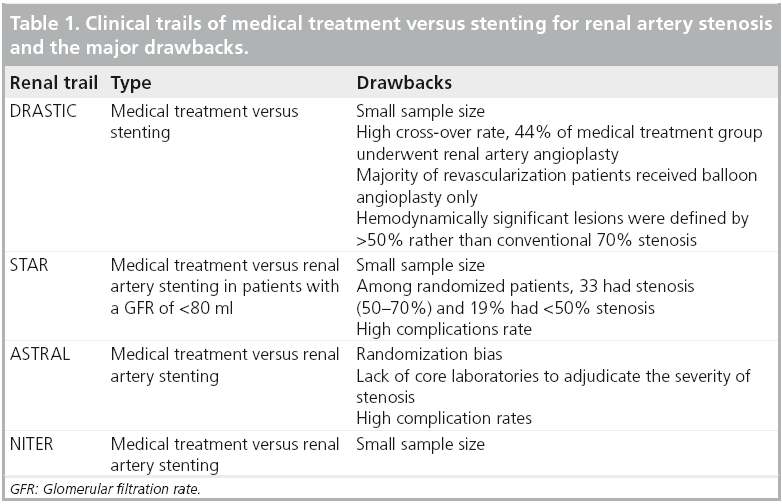
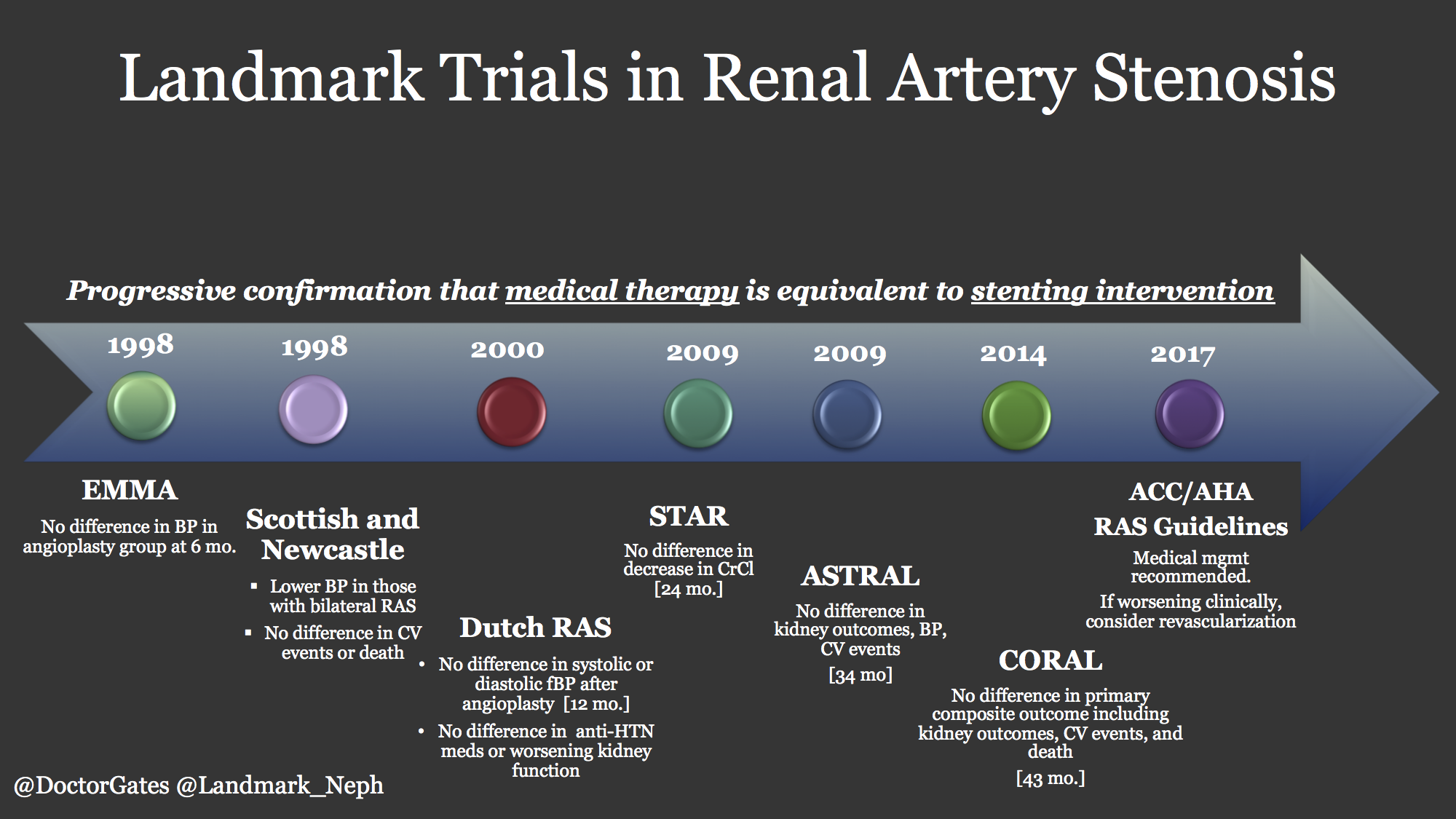
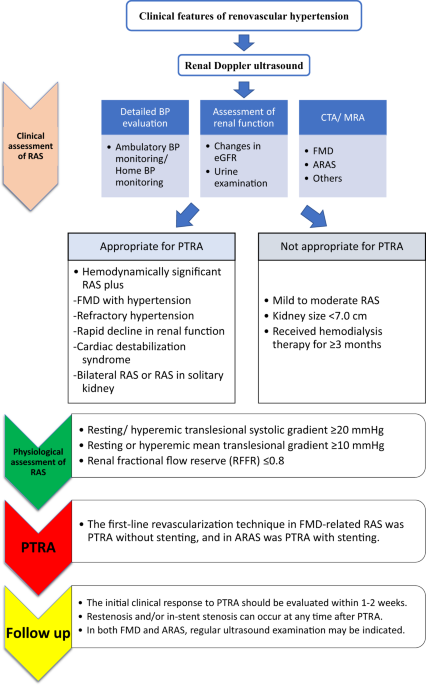
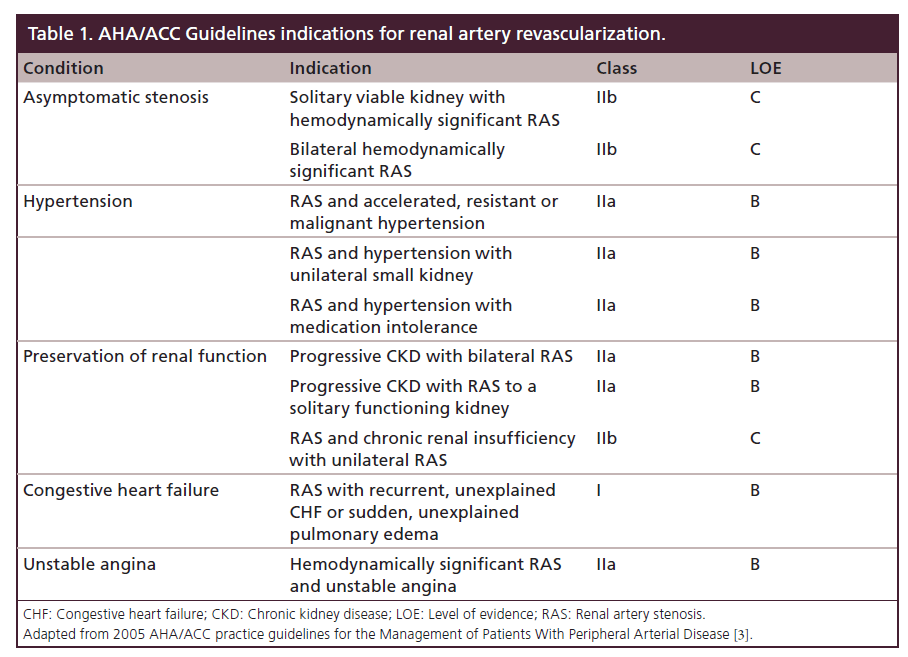
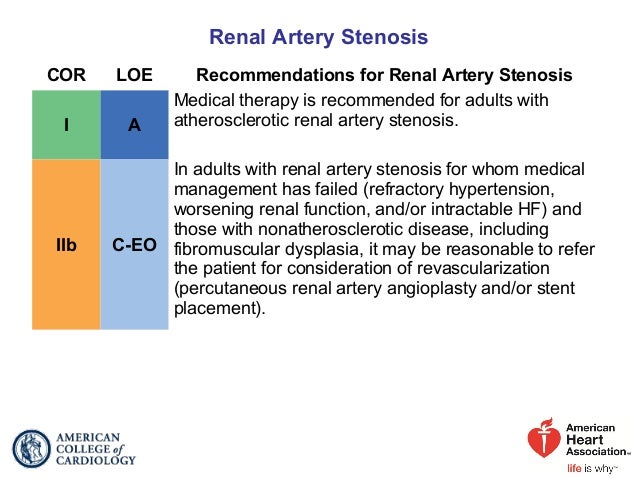
European Society for Vascular Surgery. RAS that has not led to RVH or caused a significant blockage of the artery may not need treatment. In most cases of renal artery stenosis one kidney is affected with the main vessels to the second kidney being essentially normal hence the designation unilateral disease. Renal artery angioplasty without stenting is recommended for treatment of FMD-related renal artery stenosis. Although the treatment of atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis with percutaneous angioplasty stenting and surgical revascularization has gained widespread use few prospective randomized controlled trials RCTs exist that compare these techniques with each other or against the standard of medical management alone. Treatment for RAS includes lifestyle changes medications and surgery and aims to. Renal artery stenosis RAS is a narrowing of the renal artery lumen. Stenting is not recommended unless needed because of a periprocedural dissection. This disease encompasses a broad range of pathophysiologies the two most common being fibromuscular dysplasia FMD and atherosclerotic renal artery disease1 This review will primarily focus on the epidemiology and treatment of atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis ARAS which accounts for the vast majority of cases.
Relieve the blockage of the renal arteries. University Hospitals Case Medical Center Summary. It is considered angiographically significant if more than a 50 reduction in vessel diameter is present. European Society for Vascular Surgery. However renal artery stenosis is the primary cause of hypertension ie renovascular hypertension only in certain settings. Safian RD Textor SC. RAS is associated with three major clinical syndromes.
































Post a Comment for "Renal Artery Stenosis Treatment Guidelines"